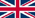
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also known as coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, occurs when the coronary arteries—blood vessels on the surface of the heart-develop atherosclerosis. This condition involves the formation of plaques that narrow or block the arteries due to various factors. The resulting restriction in blood flow causes ischemia (reduced blood supply) and hypoxia (oxygen deprivation) in the heart, causing a series of symptoms.
- The classifications of coronary artery disease
Chronic coronary artery disease(CCS): stable angina pectoris, asymptomatic myocardial ischemia, ischemic cardiomyopathy
Acute coronary syndromes(ACS): unstable angina pectoris, non-ST elevation myocardial infarction, ST elevation myocardial infarction, sudden coronary death.
- The symptoms of Angina
(1) The typical manifestation is chest pain, which often radiates to the left shoulder, left inner arm, neck, and mandibular region.
(2) The nature of the pain: pressure, tightness, boredom, choking, but generally not needle-like, knife.
(3) Inducements and factors: often occur when tired and emotional excitement, and appear at the time of fatigue. Rapid relief with rest or nitroglycerin.
(4) The chest pain gradually worsens and lasts for 3-5 minutes. It can occur once a few days or weeks, or several times a day. Note: Sometimes coronary heart disease is atypical, abdominal pain, toothache, and even finger pain can be angina pectoris.
- The manifestations of myocardial infarction
Severe and persistent chest pain, chest tightness, dyspnea, palpitation, the location and nature of the chest pain are the same as angina pectoris, can not be relieved by taking nitroglycerin, the pain lasts for more than half an hour, severe patients are accompanied by arrhythmia, heart failure, shock and consciousness disorders.
- Common causes
Hyperlipidemia: especially increased levels of low-density cholesterol, which is an important factor in atherosclerosis; In hypertensive patients, the increase of systolic and diastolic blood pressure may accelerate atherosclerosis; Diabetic patients are easily damaged because of high blood viscosity, slow blood flow and insufficient nutrients needed by myocardium. In addition, obesity, smoking, alcoholism, long-term in A stressful living environment, type A personality, lack of physical activity, there are risk factors for coronary heart disease.
5.Examination and Treatment
ECG is the most basic and simple test for coronary artery disease. It is best to do ECG at the time of onset, combined with myocardial injury markers. Echocardiography was used to assess cardiac function (ejection fraction EF) for the presence of valvular stenosis or abnormal ventricular wall motion. Chest X-rays can help identify other cardiopulmonary diseases, such as heart failure and pleural effusion. There are also tests that we can't currently perform, such as coronary angiography, which is the current gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease. Coronary CT imaging is also a non-invasive examination of more effective means of examination.
Medication: Drugs to reduce symptoms and improve ischemia, nitrates, calcium channel blockers. Drugs that improve prognosis include antiplatelet drugs, statins, beta-blockers, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors.
Revascularization Therapy: This includes two main approaches:
Interventional Therapy: Balloon Angioplasty: A procedure where a small balloon is inflated inside the coronary artery to widen the narrowed area.Stent Placement: A tiny mesh tube is inserted into the artery to keep it open after angioplasty.
Surgical Therapy:Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): A surgical procedure where a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body is used to bypass the blocked coronary artery, restoring blood flow to the heart.
6.Lifestyle Interventions
Diet pay attention to low salt and low fat light diet, eat less fat, eat less animal organs containing high cholesterol, eat more vegetables and soy products; Hypertensive patients, go to the hospital regularly, under the guidance of doctors, control blood pressure. People with diabetes should control the intake of staple foods and sweets, and increase the intake of miscellaneous grains and vegetables and soy products.smoking cessation, limited alcohol intake, and moderate physical activity. Ensure enough sleep, do not be overly nervous and emotional.